Table of Contents
Industrial boiler safety is critical for Arizona’s manufacturing and processing sectors. From food and beverage plants to energy facilities, these systems supply the steam and heat necessary to keep production running efficiently. However, this power comes with substantial responsibility. Improperly managed boilers can lead to catastrophic explosions, costly downtime, and even loss of life.
In Arizona’s hot, dry climate and diverse industrial landscape, boiler safety isn’t just a compliance issue—it’s an operational imperative. Whether your facility operates a single high-pressure unit or a complex network of boilers, understanding and implementing best practices for safety is essential for reliability, regulatory compliance, and workforce protection.
Why Boiler Safety Matters in AZ
Arizona’s industrial environment is expanding rapidly. The state’s push toward advanced manufacturing, renewable energy, and semiconductor production means more facilities are installing or upgrading high-capacity boilers. But as this expansion continues, so does the potential risk of boiler-related accidents.
1. Harsh Environmental Conditions
Arizona’s extreme climate can be tough on mechanical systems. High daytime temperatures and low humidity increase wear on boiler components, while cooler desert nights cause thermal expansion and contraction that weaken metal structures over time. Skipping regular inspections and proper monitoring allows these fluctuations to create cracks, leaks, or dangerous pressure imbalances. Maintaining boiler integrity in these conditions requires diligent safety checks and preventive maintenance.
2. Hard Water and Mineral Buildup
Arizona’s water is notoriously hard—rich in calcium and magnesium minerals that cause scaling and deposits inside boiler tubes. Left untreated, this buildup restricts heat transfer, forces boilers to work harder, and increases the risk of overheating or even rupture. Implementing an effective boiler water treatment program is one of the simplest and most effective ways to maintain efficiency, prevent accidents, and extend equipment lifespan.
3. Strict Regulatory Oversight
The Arizona Division of Occupational Safety and Health (ADOSH) and the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code enforce strict safety standards for industrial boilers. Facilities must document inspections, keep accurate maintenance logs, and ensure operators hold proper certification. Failing to comply leads to fines, operational shutdowns, and higher liability. Following these rules protects your operations and reinforces a reputation for reliability and responsibility.
4. Protecting People and Property
A boiler malfunction can escalate quickly, causing explosions, fires, or the release of scalding steam. These incidents threaten not only the physical safety of employees but also valuable assets and infrastructure. By prioritizing boiler safety through training, routine checks, and emergency preparedness, Arizona businesses can create a safer workplace and demonstrate their commitment to employee well-being.
5. Preserving Productivity and Profitability
Unsafe or inefficient boilers don’t just pose safety risks—they drain profitability. Unplanned outages, emergency repairs, and downtime from safety violations can disrupt production schedules and damage client relationships. On the other hand, safe, well-maintained boilers operate more efficiently, reduce fuel consumption, and deliver consistent output. In Arizona’s competitive industrial economy, proactive boiler safety translates directly into long-term savings and business continuity.
Core Best Practices for Industrial Boiler Operators
Ensuring industrial boiler safety begins with consistent and proactive management. Below are the most important best practices every operator in Arizona should follow.
1. Routine Inspections and Preventive Maintenance
A well-structured inspection program is the cornerstone of safe boiler operation. Operators should conduct daily, weekly, monthly, and annual checks tailored to the equipment’s design and usage intensity.
Daily inspections should include:
- Checking for unusual noises, vibrations, or leaks
- Verifying that pressure and temperature readings are within safe limits
- Ensuring safety valves and emergency shutoffs are operational
- Recording readings in a logbook for trend analysis
Annual inspections, preferably by certified professionals, should include:
- Internal visual inspection of boiler tubes, drums, and shells
- Hydrostatic testing for leaks and pressure integrity
- Burner and fuel system tuning for optimal combustion efficiency
- Verification of ASME-compliant safety devices
2. Proper Operator Training and Certification
Even the most advanced equipment poses danger if operators handle it incorrectly. Operator training is a critical part of boiler safety. Arizona requires operators to understand system mechanics, follow safety protocols, and manage emergency procedures.
Effective training programs should cover:
- Boiler design and function
- Water and fuel systems management
- Safety interlocks and pressure controls
- Shutdown and startup sequences
- Emergency response procedures
Operators must attend periodic refresher courses to stay current on technology and regulatory updates. In high-risk industries like power generation and manufacturing, ongoing training separates safe operation from catastrophic failure.
3. Implementing Comprehensive Water Treatment Programs
Water quality directly affects industrial boiler safety and performance. In Arizona, where water hardness levels are among the highest in the U.S., scaling and corrosion are serious threats.
Effective water treatment programs should include:
- Softening and demineralization to prevent scale buildup
- Deaeration to remove oxygen and prevent corrosion
- Chemical dosing for pH control and sludge conditioning
- Regular testing of feedwater and condensate return
Neglecting water chemistry leads to internal tube failures, lower efficiency, and costly unscheduled downtime. Proper treatment systems and monitoring help operators keep boilers safe and efficient.
4. Utilizing Advanced Monitoring and Control Systems
Modern industrial boilers come equipped with digital control systems that monitor performance parameters in real time. These systems allow operators to track temperature, pressure, fuel flow, and emissions from a centralized interface.
Key technologies include:
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems for remote monitoring
- Automated alarms and trip mechanisms to detect irregularities
- Sensors that provide predictive analytics on wear and tear
These innovations enhance safety and efficiency, allowing operators to act quickly before issues escalate. Retrofitting older boilers with modern control technology lowers accident risks and cuts maintenance costs.
5. Emergency Preparedness and Response Planning
Even the best-run facilities can face unexpected incidents. Every boiler operator should have a comprehensive emergency response plan that includes:
- Clear shutdown procedures in case of high pressure or low water conditions
- Evacuation routes and communication plans
- Fire suppression systems and training in their use
- Coordination with local emergency services
Regular drills and tabletop exercises ensure all personnel understand their roles in an emergency. Preparation reduces response time and limits potential damage when every second counts.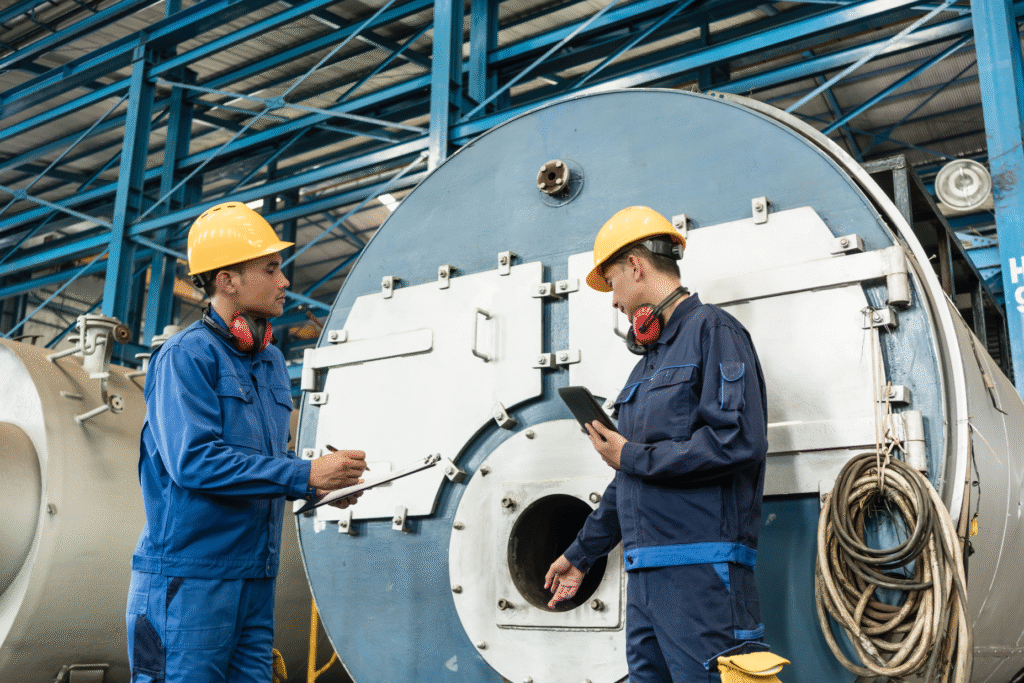
Common Boiler Safety Mistakes to Avoid
While operators often focus on maintenance and training, several overlooked mistakes can still lead to dangerous situations:
1. Ignoring Warning Signs
Strange noises, leaks, or pressure fluctuations signal potential problems in the system. Ignoring these signs lets minor issues grow into serious safety hazards. Operators must investigate and document any irregularities to prevent equipment failure or accidents.
2. Bypassing Safety Interlocks
Safety interlocks protect equipment and personnel from dangerous operating conditions. Turning off these systems to “save time” or speed up production is one of the most common causes of boiler-related accidents. Every safety mechanism must remain active and regularly tested to ensure proper function and compliance with Arizona’s safety standards.
3. Poor Recordkeeping
Accurate inspection and maintenance logs are essential for tracking the health and performance of a boiler. Without proper documentation, early warning trends may go unnoticed, leading to preventable breakdowns. Maintaining detailed records also helps demonstrate regulatory compliance during inspections and audits.
4. Inadequate Ventilation
Proper ventilation in boiler rooms is crucial for safe combustion and to prevent the buildup of toxic or combustible gases. Restricted airflow can cause incomplete fuel burning, leading to dangerous carbon monoxide accumulation or even explosions. Ensuring adequate ventilation protects both equipment efficiency and employee safety.
5. Unqualified Repairs
Certified and experienced technicians should perform boiler maintenance and repair work. Letting unqualified personnel handle repairs increases the risk of improper installation, faulty components, and future system failure. Working with licensed professionals ensures all repairs meet ASME and ADOSH safety standards.
The Role of Safety Culture in Boiler Management
Safety is not a single action—it’s a culture. Successful organizations make industrial boiler safety a shared responsibility across every level of the company.
Building a Safety-First Culture
Encourage open communication about safety concerns.
Employees should feel comfortable reporting hazards or unsafe conditions without fear of retaliation. Open communication helps management identify and correct risks before they escalate into accidents. Creating a culture of trust ensures that safety becomes a shared responsibility across the entire organization.
Recognize and reward employees who identify potential hazards.
Positive reinforcement encourages proactive behavior and shows that everyone prioritizes safety at every level. Acknowledging employees for preventing risks reinforces the importance of vigilance and accountability. Recognition programs—such as safety awards or incentives—help build long-term engagement in maintaining a safe workplace.
Conduct routine safety meetings and review incidents transparently.
Regular safety meetings provide an opportunity to discuss best practices, near misses, and lessons learned. Transparent reviews of incidents foster continuous improvement and prevent repeated mistakes. Keeping safety discussions active and inclusive ensures that every team member stays informed and committed to safe boiler operations.
Integrating safety into daily routines reduces accident risks and enhances morale and productivity.
The Future of Boiler: Innovation and Sustainability
Boiler operation in Arizona is shifting toward automation, sustainability, and digital safety systems. AI and IoT technologies enable predictive maintenance, remote diagnostics, and real-time performance optimization.
AI-Based Predictive Analytics
Artificial intelligence enhances boiler safety by detecting early signs of equipment failure. Predictive algorithms and real-time data analysis identify temperature spikes, pressure anomalies, and component wear. Maintenance teams can fix issues before they become critical, improving safety and uptime.
Automated Compliance Reporting
Automation simplifies how facilities document and report boiler safety compliance. Advanced systems generate digital records that meet ADOSH and ASME requirements, cutting manual paperwork. They save time, improve accuracy, and keep your operations ready for audits and inspections.
Energy-Efficient Retrofits
As energy costs rise, Arizona facilities invest in energy-efficient boiler retrofits. Upgrades improve combustion performance, cut emissions, and lower operating costs. Adopting cleaner technologies shows a commitment to sustainability and long-term profitability.
Hydrogen-Ready and Hybrid Boilers
The shift to renewable energy increases demand for hydrogen-ready and hybrid boiler systems. These units currently run on traditional fuels and will adapt to cleaner energy sources later. Preparing today helps Arizona industries future-proof operations and meet the state’s sustainability and carbon-reduction targets. Investing in these systems improves safety and supports corporate sustainability and environmental goals.
Conclusion
Industrial boiler safety in AZ goes beyond passing inspections. It builds resilient, efficient, and responsible operations that prioritize people and performance.
Implementing thorough maintenance programs, operator training, and advanced monitoring systems helps facilities achieve reliability while reducing risks. As industrial growth accelerates, safety must evolve with innovation. When upgrading systems or installing new ones, keep in mind that safe boilers drive productivity.
Take the Next Step Toward Safer, Smarter Boiler Operations
At Patriot Boiler, we specialize in helping Arizona’s industrial facilities maintain the highest safety and efficiency standards. Our certified experts provide:
- Detailed boiler safety audits and risk assessments
- Custom operator training programs
- Scheduled preventive maintenance plans
- Compliance support with local and national regulations
Don’t wait for costly downtime or safety violations to disrupt your operations.
Contact Patriot Boiler today to schedule your on-site boiler safety evaluation and ensure your facility is running safely, efficiently, and fully compliant.
📞 Call us: 480-797-9349
🌐 Visit: Patriot Boiler